What is Lean Product Management and How to Apply It?
For every product, customers expect frequent, high-quality updates, while businesses must innovate rapidly to stay ahead of the curve. This is where lean product management comes into play - a methodology that empowers teams to create customer-centric products with minimal waste and maximum impact.
This guide dives deep into what lean product management is, why it matters, and how to implement it effectively.
What is the Lean Methodology?
Lean methodology originated in manufacturing, particularly in Toyota’s production system, which focused on minimizing waste, maximizing value, and continuous improvement. It revolves around the core idea of delivering what customers want, without unnecessary frills while constantly iterating and improving the process.
This approach revolutionized manufacturing and has since been adapted to various industries, including software development and product management.
What is Lean Product Management?
Lean product management takes the principles of lean methodology and applies them specifically to the role of product managers. In essence, it’s about managing the product life cycle with a mindset of reducing waste in time, effort and resources, while maintaining a laser focus on delivering customer value.
It encourages experimentation, validated learning, and frequent iterations to ensure that teams are always working on building the most important features.
Example:
To illustrate the difference between traditional and lean approaches, let's consider the development of a new feature for a mobile banking app:
Traditional approach:
- Extensive market research and planning (3 months)
- Detailed feature specification (1 month)
- Development of full feature set (6 months)
- Quality assurance testing (1 month)
- Launch of complete feature (1 day)
- Post-launch analysis and iterations (ongoing)
Outcome:
This approach is thorough but slow. By the time the feature is released, market dynamics may have shifted, and the assumptions made at the start could be outdated, leading to high costs and potential customer dissatisfaction.
Lean approach:
- Customer interviews and problem validation (2 weeks)
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP) design (1 week)
- Rapid development of core functionality (2 weeks)
- Release to a small user group (1 day)
- Gather feedback and analyze usage data (1 week)
- Iterate based on learnings (repeat steps 3-6 in 2-week cycles)
Outcome:
The lean approach gets the core feature to market faster, allowing for real-time learning and adjustments. Instead of assuming what users want, it validates assumptions continuously and ensures that the product evolves based on actual usage data, minimizing wasted effort.
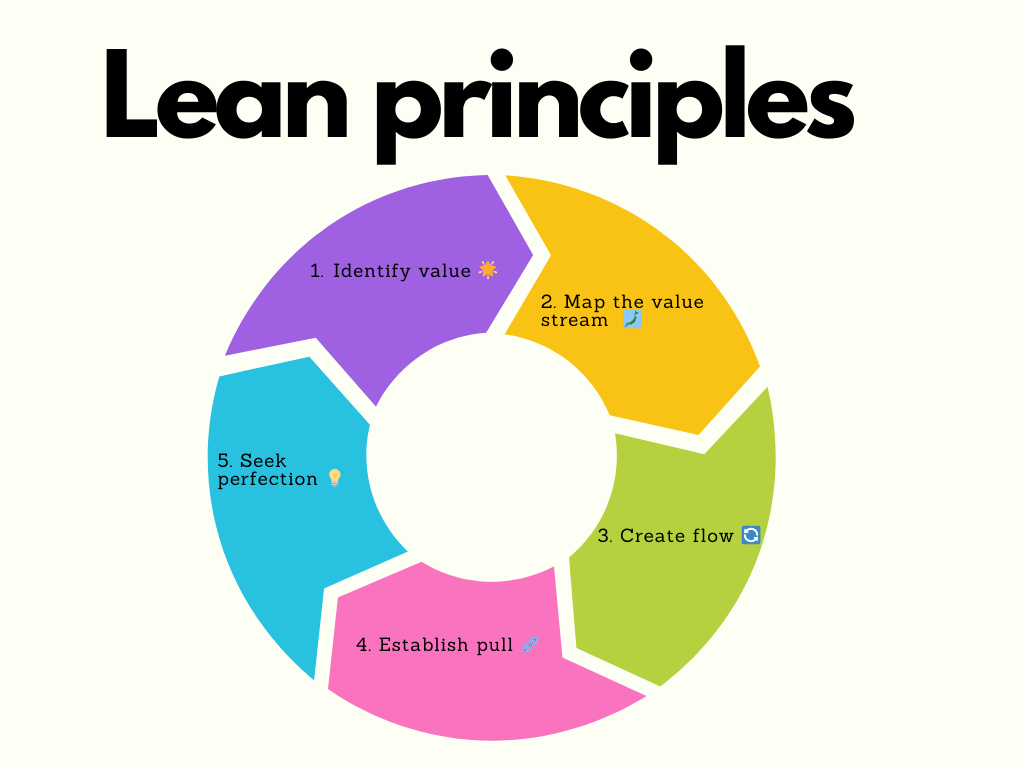
Lean Principles in Product Management
Five key principles guide lean product management:
- Define value: This means deeply understanding your users' needs and problems. Techniques like user interviews, surveys, and observational studies help identify what customers truly value.
Practical Tip: Create user personas and journey maps to visualize your customers' experiences and pain points.
- Map the value stream: Visualize your entire product development process, from idea generation to user adoption. This helps identify bottlenecks and unnecessary steps.
Practical Tip: Use tools like value stream mapping or process flow diagrams to document and analyze your current workflow.
- Create flow: Eliminate obstacles that slow down your development process. This could involve breaking down silos between teams, reducing handoffs, or implementing agile methodologies.
Practical Tip: Implement daily stand-up meetings to quickly identify and address blockers in your team's workflow.
- Establish pull: In product management, this means building features in response to actual user demand rather than perceived needs.
Practical Tip: Use techniques like feature flags to release new functionality to a subset of users and gauge interest before full deployment.
- Seek perfection: Continuously gather feedback and make incremental improvements to your product and processes.
Practical Tip: Implement regular retrospectives to reflect on what's working well and what can be improved in your product development cycle.
Case Studies of Lean Product Development
1. Spotify: The Squad Model
Spotify revolutionized its product development by implementing the "Squad" model, which emphasizes agility and autonomy within cross-functional teams.
Key elements:
- Squads: Small, autonomous teams responsible for specific features. Each squad operates like a mini-startup, making independent decisions about what to build and how to build it.
- Tribes: Groups of squads working towards a common mission, facilitating collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Chapters and Guilds: Communities that promote skill development and knowledge exchange across squads.
Outcomes:
- Faster innovation: The autonomy of squads led to quicker responses to user feedback and market demands.
- Enhanced user focus: Squads tailored their efforts to meet specific user needs, resulting in improved product alignment with customer expectations.
- Increased employee satisfaction: The model fostered a culture of ownership and engagement among employees, contributing to higher job satisfaction.
2. Dropbox: Lean Experimentation
Dropbox utilized lean startup principles to validate and refine its product offerings and enhance user engagement.
Key elements:
- MVP (Minimum Viable Product): Dropbox launched with a simple MVP that allowed users to understand the core functionality of file sharing and storage without overwhelming features.
- User feedback loops: Continuous collection of user feedback helped Dropbox iterate on its product quickly, ensuring that enhancements were aligned with user needs.
- Experimentation culture: Dropbox fosters a culture where teams are encouraged to run experiments to test new features or changes before full-scale implementation.
Outcomes:
- Effective user engagement: The initial MVP approach led to significant user acquisition as it addressed essential needs without unnecessary complexity.
- Agile iteration process: The emphasis on user feedback allowed Dropbox to adapt its offerings rapidly, improving retention rates over time.
- Scalable growth model: By validating ideas through minimal viable products, Dropbox effectively scaled its features based on real user demand.
3. Amazon: Customer-Centric Approach
Amazon employs a lean product management approach centered on customer obsession, driving innovation through its unique organizational practices.
Key elements:
- Working backwards process: Product development starts with writing a press release and FAQ for the proposed product. This ensures clarity on the customer benefits before any development begins.
- Two-pizza teams: Small, cross-functional teams (no larger than can be fed with two pizzas) are empowered to make decisions quickly and efficiently.
- Data-driven decisions: Amazon relies heavily on data analytics to inform product development and improve customer experience continuously.
Outcomes:
- Rapid product development: The working backwards approach allows for quick iterations based on customer feedback.
- High customer satisfaction: By focusing on customer needs from the outset, Amazon consistently delivers products that resonate with users.
- Innovation at scale: The small team structure enables rapid experimentation and scaling of successful products like Amazon Prime and AWS.
These case studies illustrate how each company has successfully implemented lean product management principles tailored to their unique contexts, leading to enhanced innovation, customer satisfaction, and overall business success.
Why is Lean Development Important?
Adopting lean product management practices offers several key benefits:
- Faster time-to-market: In lean product management, the focus is on creating MVPs and iterating quickly. Instead of spending months or years developing a full-featured product, teams release a basic version with core functionality much sooner.
- Reduced development costs: Lean practices emphasize building only what's necessary, which significantly cuts down on wasted resources. This principle applies to both time and money.
- Improved product-market fit: Lean product management emphasizes continuous user feedback and data-driven decision making. This ongoing dialogue with users ensures that the product evolves to meet actual market needs.
- Enhanced team collaboration: Lean methodologies often involve cross-functional teams working closely together, breaking down traditional silos between departments.
- Better risk management: By testing ideas early and often, lean practices help identify potential issues before they become major problems.
According to a study by the Lean Enterprise Institute, companies implementing lean practices saw a 50% reduction in product development time and a 25% increase in productivity.
How to Apply Lean in Product Management?
Applying lean principles to your product management process requires a strategic yet flexible approach.
- Start small with an MVP: Focus on delivering the minimum features needed to solve a problem for early users. This could be as simple as a demo, prototype, or a basic version of the product.
- Iterate based on feedback: Once the MVP is in the hands of users, gather feedback and iterate. Each iteration should be informed by real data, not assumptions.
- Prioritize ruthlessly: Use customer value as your North Star. Every feature, experiment, or resource should be weighed against its ability to deliver value.
- Build cross-functional teams: Collaboration is key in lean product development. Involve engineering, design, marketing, and even sales early in the process to ensure alignment and rapid feedback cycles.
- Create a culture of experimentation: Encourage teams to take calculated risks, test hypotheses, and fail fast. Learning quickly from failures will help guide the next set of actions.
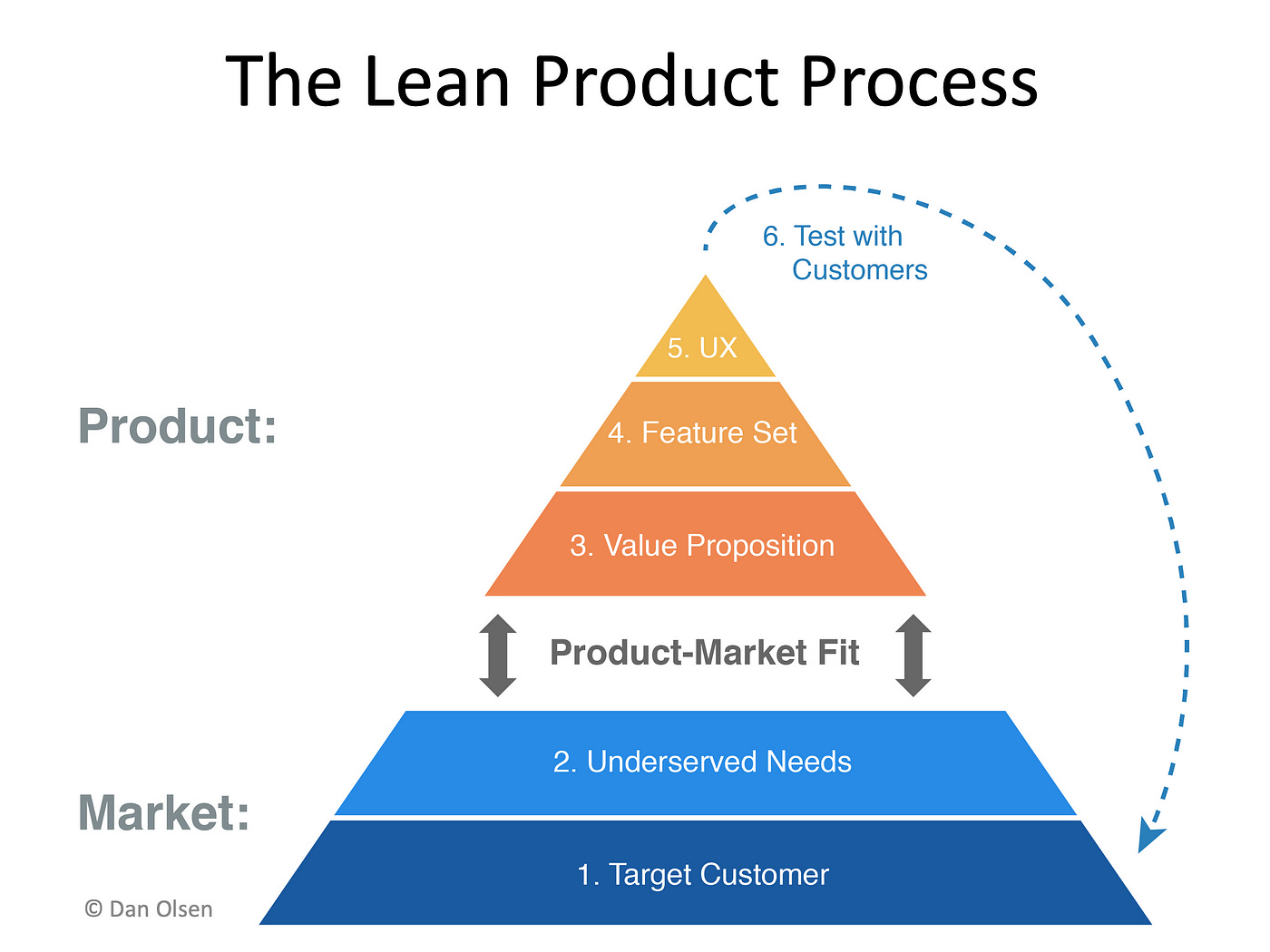
source: Dan Olsen
The Product Manager’s Role in Lean Product Development
In a lean product management environment, the product manager plays several crucial roles:
- As a facilitator: Ensure smooth communication and collaboration between cross-functional teams.
- As a decision-maker: Use data and user insights to prioritize features and make informed product decisions.
- As a customer advocate: Continuously represent the voice of the customer in all product discussions.
- As a metrics champion: Identify and track key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with business goals and user needs.
- As a change agent: Build a culture of experimentation, learning, and continuous improvement within the team.
Key Takeaways For Product Managers
Lean product management is a powerful approach that can transform your product development process. Here are the key points to remember:
- Focus relentlessly on delivering value to your customers
- Embrace rapid experimentation and learning
- Use data to drive decision-making
- Continuously seek to eliminate waste in your processes
- Foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement
To start implementing lean product management in your organization:
- Begin with small, low-risk experiments
- Invest in tools and processes that support rapid iteration
- Educate your team on lean principles and their benefits
- Celebrate learning, even from "failed" experiments
- Regularly review and refine your processes
Suggested read: Book - The Lean Startup" by Eric Ries
Found this useful?
You might enjoy this as well

AI Product Manager Salary in India 2025 : The Career That Pays to Think Smarter
Discover 2025 AI Product Manager salaries in India from career paths to skill growth, real pay data, and the future of AI-first PM roles.
November 11, 2025

APIs for Product Managers: A Non-Technical Guide
A non-technical introduction to APIs, specifically for product managers. Learn the core concepts and their importance in product development.
July 15, 2025

APIs for Product Managers: A Non-Technical Guide
Learn essential API concepts, terminology, and how APIs impact product strategy. This guide helps Product Managers leverage APIs for better product development.
July 15, 2025